
How is Flexible Graphite Used in Fuel Cells?
CO2 Emissions and Alternative Fuels
Worldwide industrial nations are showing concern over CO2 emissions and want to take action towards reducing the level of carbon gas released into the atmosphere. Finding alternatives to fossil fuel use is one of the biggest concerns facing our generation today. What are the alternatives to fossil fuel use?
Thankfully there are several alternatives to fossil fuels such as wind power, solar energy, biofuels, hydrogen energy, and nuclear power. The focus of this article is on hydrogen energy and hydrogen fuel cells.
Types of Fuel Cells
There are five different types of fuel cells:
- Solid Oxide
- Molten Carbonate
- Phosphoric Acid
- Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) or Solid Polymer Membrane (SPM)
- Alkaline
A hydrogen fuel cell is a type of proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell.
How Does a Hydrogen Fuel Cell Work?
All fuel cells contain an anode, cathode, and an electrolyte. Below is a simplistic diagram of a simple hydrogen fuel cell, which is a type of PEM fuel cell.
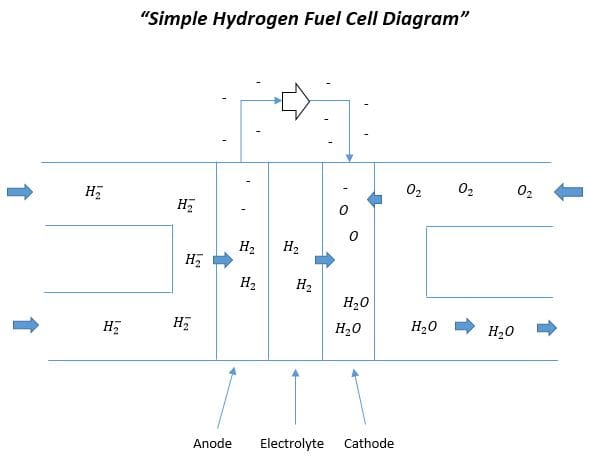
Hydrogen gas enters the fuel cell coming in contact with an anode. As the hydrogen gas passes from the anode to the outer surface of the electrolyte hydrogen gas becomes unbounded and electrons are stripped off. Positively charged hydrogen continues to pass through the electrolyte while the electrons travel parallel up the anode to an exterior circuit. At the same time oxygen gas is injected from the cathode end of the fuel cell. Oxygen passes through the outer layer of the electrolyte from the cathode side and meets the positively charged hydrogen. The exterior circuit provides power for the load but also brings current back down to where the electrolyte meets the cathode. The electric current combined with the residing hydrogen and oxygen results in the byproduct of this power generating process, which is water. This process will continue to provide power as long as hydrogen and oxygen are supplied.
How is Flexible Graphite Used in a Hydrogen Fuel Cell?
Flexible graphite is used to make the bipolar plates that make up the anode and cathode of a fuel cell. Flexible graphite serves the dual purpose of being electrically conductive parallel to its surface and highly resistant to corrosion at high temperatures. It is necessary to reinforce flexible graphite with a resin since its structure is vulnerable at high temperatures.
Fuel Cells Can Be Part of the Solution
Fuel cells have been a big buzz in the transportations industry today, but there are a broad range of applications outside the transportation industry. Hydrogen fuel cells can be used to power buildings and electronics. It can be used as a back-up for power plants, data storage centers, and hospitals.
Finding an answer to the fossil fuel puzzle will not result in one solution. The most likely solution will be to use a combination of power alternatives, like solar, wind, nuclear, and battery power. Fuel cells will only be one part of this solution, but it will be a significant part. And flexible graphite will be a key component in producing this efficient and effective technology.
